10x content: content that is 10x better than the highest-ranked content in search engine results
- Always strive to create 10x content so Google will rate it highly in search results.
Alt text/alt tag: text describing an image, which is read aloud by a screen reader and appears when the image does not load
- Alt text is required for all images uploaded to our website.
- Google reads alt text, so it's important to include keywords if possible.
Crawl: the process in which search engine robots (called crawlers or spiders) find new and updated content on the web
- Crawlers look at all types of content like webpages, videos, images, PDFs, etc.
Domain authority: a search engine ranking score developed by Moz to gauge how high a website will rank in search engine results pages
Duplicate: content that is copied and published using a different URL, which should be avoided because Google will choose only one version to show in its search results and might choose the wrong version If duplication is unavoidable, ask the web team to implement either a noindex tag or a canonical tag to tell Google which one the "master copy" is.
- Robots noindex tag: tells search engines not to index the page
- Canonical tag: tells search engines this URL is the only version of the page that exists
- Canonical tags can be self-referential. In other words, it's fine if you put a tag on your article that points to that same article.
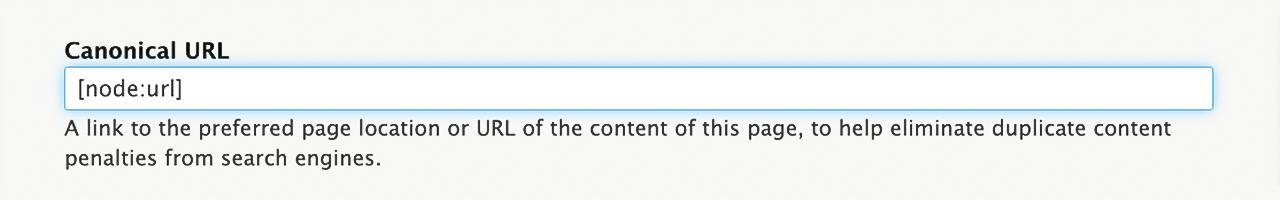
- How-to: Writers can ask publishers who are duplicating their content to include a canonical tag in their article to tell Google to prioritize the original. The publisher must include the original article's URL in the "Canonical URL" section of their article. In SiteFarm, users can find this section in the right-side navigation: SEO > Advanced > Canonical URL.
Header/heading tag: titles of sections that improve the readability and scannability of a page
- Written as H1, H2, H3, etc.
- There should only be one H1 tag.
- The general rule is to not go beyond H4 because the text becomes too small to be accessible.
Indexing: when a search engine finds and adds web content to its index so that it appears in search results
- Search engines use crawlers to find web content.
- Just because web content is indexed does not mean it will rank highly. If content consistently ranks low in search results, it can be unindexed.
Keyword: important words and phrases users search for
- Your primary keyword should be your most important keyword — the word or phrase your intended audience is most likely to search for.
- Secondary and tertiary keywords have less importance than the primary keyword, but they should still be included on the page and in headers.
Keyword map: mapping keywords to content to optimize that content based on keyword research
Keyword stuffing: when a keyword is used an unusually high amount of times to manipulate a page or site's ranking in search engine results
- Avoid doing this as search engines will penalize your content and give it a low rank or unindex it entirely. It could even get your website temporarily or permanently banned.
Meta description: a 155-160 character summary of the page that appears in search results
- Be sure to include keywords in the meta description. This does not affect search ranking, but the keywords will be bolded and will catch users' attention if they have used those words in their search.
- Example: Get a guaranteed spot at UC Davis. Find out the eligibility requirements, application process and admission timeline for UC Transfer Admission Guarantee (TAG).
- How-to: Click "Edit Summary" next to "Body" to open the summary text box. Put the meta description here.
MSV: short for "monthly search volume," which means how many times a keyword has been searched for per month
- Keywords with higher MSV are usually harder to compete for, so a combination of high and low MSV keywords will help content gain more visibility.
Readability/reading level: the level at which the audience is able to read your content
- The general goal is to write at a 7-8th grade level, but if the content is naturally difficult to grasp, higher levels are okay. Always avoid going above college level.
- You can determine the reading level of your content using Word.
Discover how to find reading level in Word
SEO: search engine optimization
- Technical SEO: technical optimizations that help search engines crawl and index our site (like using proper header tags)
- On-page SEO: content optimizations that help our pages rank higher in search results and gain more traffic (like implementing relevant keywords in articles)
- Off-page SEO: optimizations that happen outside of our site (like when another website mentions us or links to us)
SEO health: how well your content is following SEO best practices
SERP: short for "search engine results page"
Title tag/page title: a 55-60 character title of your content that appears in search results
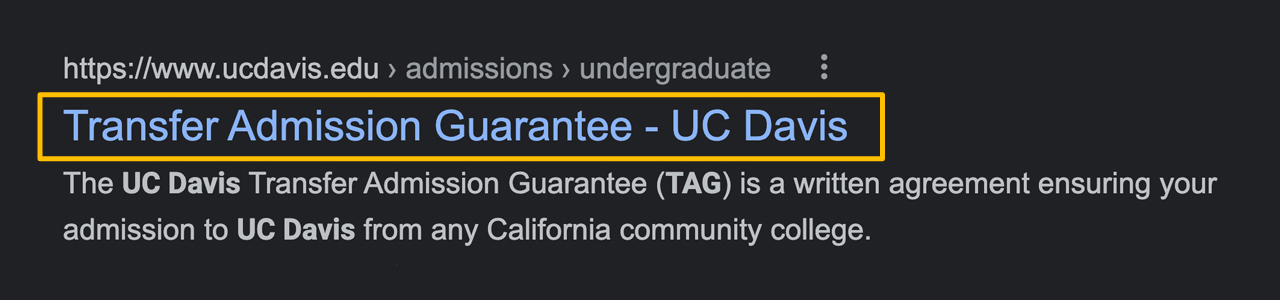
- You can make this title different from the title of your article.
- Ideally, a title tag should look like "Title | UC Davis"
- Example: Transfer Admission Guarantee (TAG) Complete Guide | UC Davis How-to: Click "SEO" in the right navigation. Type your page title in the "Page title" section. If you'd like the page title to match your article title, leave it as is.
![A screenshot of the title tag section in SiteFarm. The description says "The text to display in the title bar of a visitor's web browser when they view this page. This meta tag may also be used as the title of the page when a visitor bookmarks or favorites this page, or as the page title in a search engine result. It is common to append '[site:name]' to the end of this, so the site's name is automatically added. It is recommended that the title is no greater than 55 - 65 characters long, including spaces."](/sites/g/files/dgvnsk6246/files/media/images/page-title-uc-davis-2.jpg)